Doctranslate.io Receives AI Software Recognition from a Popular B2B Review Platform
A reputable review website commends Doctranslate.io for its exceptional performance as AI software.
FinancesOnline, a well-known site that reviews software, gave Doctranslate.io the Rising Star Award. AI software brands that have steadily gained loyal customers and pleased users for a while now are given this award.
FinancesOnline created a comprehensive review of Doctranslate.io and discussed its effectiveness as an AI tool. Based on the software experts’ opinion, this AI software is a cloud-based tool for translating documents that work well in today’s busy and multilingual world.
With voice analysis, summary, and PDF scanning, DocTranslate.io simplifies document translation. Doctranslate.io is a dependable resource for accurate translations because of its emphasis on security and user assistance.
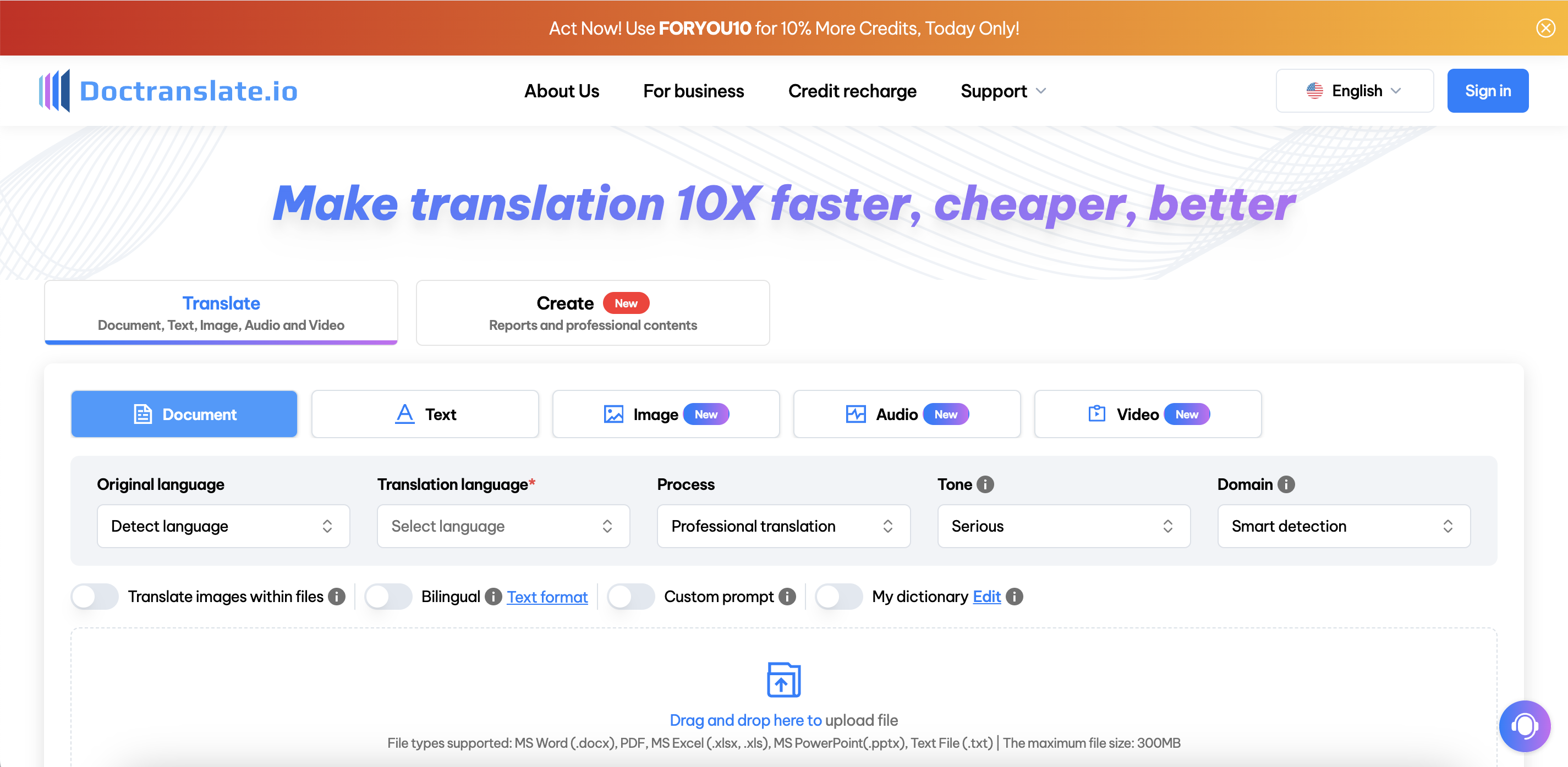
Software experts from FinancesOnline commend the AI software’s advanced features. It is easy to use and open to everyone. Some features include localization automation, bilingual machine translation, permission management, quality control, terminology management, translator database, website translation, multiple format support, and translation analytics.
There are also benefits to this AI tool that make it easy for people to use it whenever they want. First, DocTranslate.io can translate between English and over 85 other languages, including Spanish, French, German, Japanese, Vietnamese, and more. This makes it easier for people in different markets to talk to each other and expands the spread of the website worldwide.
Second, DocTranslate.io can handle many file types, like Word, Excel, PDF, and PowerPoint, which makes translation easier. Users can share files in the best formats without worrying about compatibility issues. This allows professionals to keep their original plans and designs so that all translated materials look consistent and professional.
Third, DocTranslate.io lets users change the translation results based on their preferred tone and domain. With this feature, businesses can ensure their messages are helpful and exciting to those they want to reach. For better-translated content, users can change words and phrases to fit their business.
Lastly, DocTranslate.io uses cutting-edge AI technology to deliver texts quickly and accurately, significantly reducing wait times compared to traditional methods. Automating different translation processes helps businesses meet tight targets while streamlining their work and focusing on more critical tasks.
As technology improves, more AI software that helps get work done comes out. According to Statista, different industries spent a lot of different amounts on artificial intelligence (AI) in 2023. Banking and retail businesses spend the most on AI. It was expected that all industries would pay 154 billion U.S. dollars for AI-based systems in 2023.
The following features and benefits are what review sites look for in their list of top AI software today.
The Doctranslate.ai team would like to thank FinancesOnline for giving them recognition for their excellent performance as an AI software. It truly is a privilege and an opportunity of a lifetime.
We appreciate our devoted clients’ unwavering faith in our company. Our staff is eager to continue serving you all for many more years. We’ll try our hardest to continue being committed and offering top-notch services.


